Consciously changing lifestyles, such as healthy eating, regular participation in sports activities, socializing, and adequate rest, are all ways we can prevent premature aging. But most importantly, over the years, many scientists have claimed that some breakthroughs have a huge impact on extending human lifespan and vitality, with glutathione being particularly prominent.
What exactly is glutathione?
Glutathione is a naturally occurring molecule found in every cell of our body. It is composed of three amino acids – cysteine, glycine, and glutamic acid.
It is involved in many cellular functions, such as stress defense, detoxification, and cell signaling. Glutathione also affects DNA and protein synthesis, amino acid transport, gene expression, and regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Therefore, maintaining optimal levels of glutathione is crucial for protecting our body’s balance.
The imbalance of glutathione is related to the progression of many diseases, such as cancer, cystic fibrosis, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, inflammation, immune and metabolic diseases. Regardless of the type of chronic disease, the level of glutathione will be at a lower level.
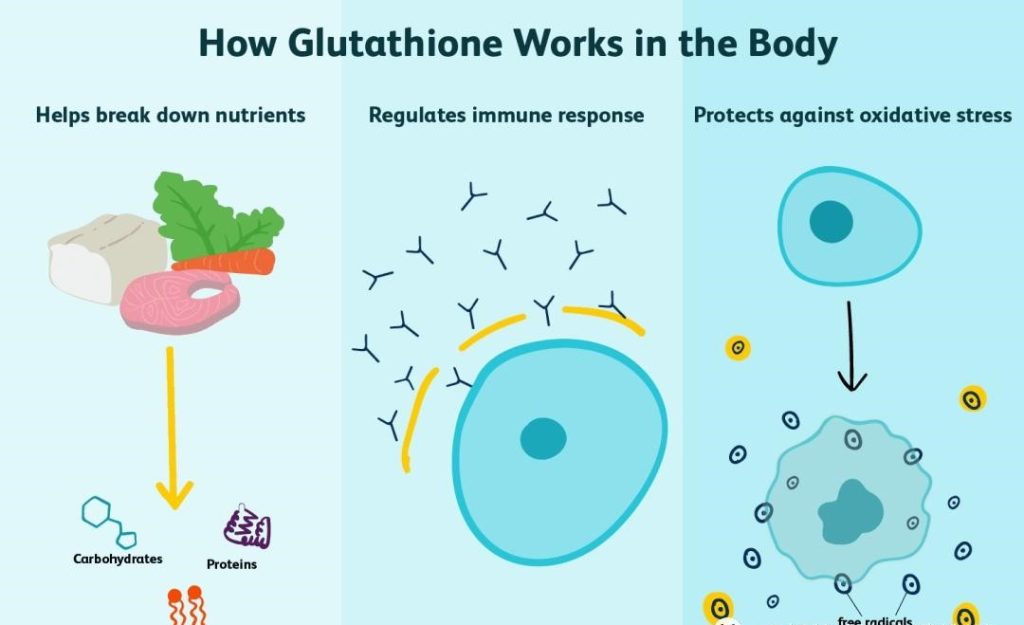
Can glutathione really reverse aging
Why is glutathione said to be the strongest endogenous antioxidant
01 Glutathione – Antioxidant Master
Glutathione is known as the master of antioxidants for no reason. It exists in every cell, but is most concentrated in the liver (the liver is the main organ for biosynthesis and detoxification in the human body). It can also regenerate other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and E.
Glutathione can eliminate toxins and free radicals in cells, reduce the amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and avoid molecular and DNA damage caused by oxidative stress. The presence of ROS may also trigger mutations in tumor suppressor genes.
In addition to protecting us from oxidative stress, glutathione also helps detoxify drugs. Long term use of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) has many negative effects, including increased cytotoxicity and elevated ROS levels, accompanied by a decrease in glutathione levels.
Glutathione is also an effective chelating agent responsible for transporting and excreting toxic heavy metals in the body. We absorb these substances through food intake and exposure to certain chemicals, which may cause neurological and cognitive impairments as well as cell damage.
02 Glutathione is beneficial for the skin
Glutathione has become more and more popular because of its skin care function. Although there is still controversy about which type of application is most beneficial to the skin, glutathione ingredients can be seen in many products now, such as lotion, face cream, sublingual spray, capsules, injections and so on. People use these products to get youthful glow.
In addition to detoxification and reducing free radicals, one of the anti-aging effects of glutathione is that it can protect skin cells from long and medium wave ultraviolet radiation.
In fact, against medium wave ultraviolet radiation, glutathione provides almost the same level of defense as nucleotide excision repair, which is an automatic DNA repair mechanism for damaged cells. Therefore, researchers believe that the main role of glutathione in human skin cells is to protect them from the cytotoxic effects of sunlight.
When it comes to repair and protection, glutathione plays a crucial role in repairing wound tissue. In 2007, an experiment published in Biofizika showed that dinitroiron complexes and glutathione accelerated animal wound healing. Glutathione has also been proven to reduce wrinkles and dry spots, which can make us look older than our actual age.
03 The anti-inflammatory effect of glutathione
Inflammation is necessary for the human body and can even help resist invading antigens, but it is also associated with many chronic diseases, most of which are common in the older people.
Inflammation plays a crucial role in the aging process, and as we age, our body no longer effectively produces the cytokines necessary to regulate immunity, inflammation, and produce new blood cells.
The good news is that when we reach the optimal level of glutathione through supplementation, we have a better chance of reducing or eliminating inflammation.
Some studies on pulmonary inflammation have confirmed the protective and therapeutic effects of glutathione on oxidative lung injury and inflammation.
The results indicate that glutathione is beneficial for cellular health as it can significantly reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in subjects.
Glutathione regulates NF kB activity, which is responsible for the expression of pro-inflammatory genes.
04 Glutathione is beneficial for the intestines
One of the effects of glutathione’s anti-inflammatory ability is its impact on intestinal health. A study on the role of glutathione peroxidase in gastrointestinal inflammation suggests that insufficient glutathione activity in the intestine can lead to acute and chronic inflammation, which is common in intestinal leakage syndrome.
Glutathione helps to control various digestive system diseases, including irritable bowel syndrome, gastroenteritis, ulcerative colitis, chronic diseases, and malabsorption syndrome. It also protects various organs of the digestive tract from inflammation, infection, and cell damage, preventing gastritis, ulcers, and gastrointestinal cancer, as it can protect the gastric lining from oxidative stress, antigens, and cancer cells.
05 Glutathione is beneficial for cardiovascular health
Glutathione can help protect the heart by reducing oxidative stress and promoting normal cardiovascular function.
In animal experiments, glutathione deficiency leads to abnormal function and structure of blood vessels and heart. Another study also shows that glutathione level in carotid atherosclerotic plaque is reduced or missing.
The study also found that deficiency of glutathione activity is common in patients with coronary artery disease.

Various research results have shown that glutathione can serve as a marker for preventive antioxidant therapy and cardiovascular event risk in patients.
06 Antimicrobial efficacy of glutathione
A study published in the journal Drugs In Dermatology in 2013 tested the efficacy of glutathione as an antibiotic using strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from human skin and soft tissue.
Experiments have shown that when the level of glutathione is raised to five times the normal level, an acidic environment is formed, completely preventing bacterial growth. The same study also tested whether glutathione has toxic effects on animal cells, especially when its levels increase.
The results indicate that even at the highest test concentration (16 times physiological level), it is still relatively non-toxic.
Another evidence of the antibacterial effect of glutathione is the efficacy of inhaled glutathione therapy for treating patients with cystic fibrosis.
A study published in Langmuir magazine showed that silver nanoparticles coated with glutathione have antibacterial activity against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.
07 Glutathione enhances immunity
When the level of glutathione is at its optimal state, the lymphocytes required to maintain the immune system perform best, and glutathione is also necessary for lymphocyte replication.
The white blood cell function and good levels of glutathione in healthy centenarians prove this,
which may explain why these people can live to a very old age.
On the contrary, the high consumption of cysteine and glutathione is a characteristic of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Lack of antioxidants is associated with frequent and severe infections, leading to increased mortality rates.
As cells age, they begin to lose their ability to self repair and protect. That’s why maintaining high levels of glutathione can have a significant positive impact on the ability to resist diseases.
Another reason why glutathione has anti-aging effects is that it can combat age-related oxidative stress and inflammation,
which can increase our susceptibility and vulnerability to infection.
Do you know that breast milk also contains glutathione? This makes this “liquid gold” more effective in enhancing immune system function.
08 Glutathione maintains bone health
One of the many physiological changes brought about by aging is the decrease in bone density. For many people, it can lead to osteoporosis and may increase the risk of fractures.
There are many factors that can lead to premature bone weakness. One of them is oxidative stress, which is where glutathione plays a crucial role.
As the main antioxidant, glutathione can prevent or delay bone loss.
The stronger our immune response, the stronger our bones will be. In this regard, glutathione indirectly helps maintain optimal bone density, whether young or old.
09 Glutathione is beneficial for enhancing strength and endurance
In a Japanese study published in the Journal of the International Society for Sports Nutrition,
glutathione supplements said to enhance the muscle’s ability to utilize oxygen while reducing fatigue during intense physical activity or exercise.
In an experiment, healthy participants divided into several groups, one group asked to take a daily glutathione supplement,
while the other group given a placebo, and both groups asked to exercise for one hour a day.
The results showed that the group taking glutathione performed better because they had less lactate accumulation in their muscles and less muscle fatigue.
Due to the fact that glutathione also supports cardiovascular and pulmonary functions,
the optimal level of glutathione allows us to perform more physical tasks without quickly becoming exhausted.
10 Glutathione is beneficial for cognitive health
At optimal levels of glutathione, aging does not necessarily mean a decline in cognitive ability.
Glutathione depletion is closely related to the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. When the brain continuously consumes 20% of the body’s intake and absorption of oxygen, reactive oxygen species (ROS) also produced. Therefore, detoxification within brain cells is crucial, and it is in this field that glutathione plays a crucial role.
One of the characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease is the accumulation of TDP-43 protein in the nervous system, which can further reduce glutathione levels. Fortunately, glutathione supplements have the potential to slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. In fact, clinical studies have shown that increasing glutathione levels can improve the memory of animals with this disease.

Just like Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease caused by oxidative stress,
which is why glutathione has a similar effect on patients with this disease. In addition, glutathione can also improve mitochondrial health, which is a hallmark feature of degenerative diseases.
Finally, a study on Parkinson’s disease suggests that in the preclinical stage of Parkinson’s disease,
the same brain region has lower levels of glutathione. Therefore, scientists have invented a drug called 3,4-dihydroxybenzophenone, which helps prevent this disease by increasing levels of glutathione.
11 Glutathione is beneficial for sleep
The circadian rhythm changes sharply with age, and compared to deep sleep,
older people have shorter sleep time and longer time in the shallow sleep stage.
Fortunately, glutathione can help you achieve a complete and energetic sleep.
In a study published in the journal Chest Dishes and Allied Sciences,
glutathione antioxidant therapy combined with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) significantly improved the condition of patients with sleep apnea.
After only two days of treatment, patients can sleep longer and have better sleep quality.
Sleep studies also indicate that oxidative stress can affect the duration and depth of sleep.
By clearing reactive oxygen species through glutathione, the body can obtain all the benefits of sleep.
12 Glutathione is beneficial for overall longevity
Overall, glutathione is indeed a miraculous molecule. It may not keep us forever young, but it definitely allows us to live longer. More importantly, it helps us enjoy life.
An experiment conducted by the University of Louisville attempted to demonstrate the longevity effect of glutathione on mosquitoes. When they increased the level of glutathione in insects by 50-100%, their lifespan increased by 30-38%.
A similar enzyme activity study conducted in Denmark showed that the levels of glutathione in older people aged 100-105 were higher than those aged 60-79.
Higher levels of glutathione associated with lower cholesterol, lower body mass index, fewer diseases, higher self-assessment of health, and lower blood pressure.


