NMN, a term frequently mentioned in recent years, is not a “panacea”, but it might be a “miracle drug”.
Introduction
When do we start to realize that we are getting old? Was it the slight creaking of the knees when squatting down and getting up, or was it that one day when looking in the mirror, the fine line at the corner of the eye didn’t disappear after a good sleep?
Perhaps working until ten o ‘clock at night, one finds that staying up late is no longer a capability but a punishment for the body the next day.
Aging is never something that happens overnight. It quietly emerges in every moment of exhaustion and every moment when one is too lazy to explain.
And perhaps you have just been too tired for too long and forgotten that your body, in this era, can actually be gently repaired.
It is a hope that is gradually being confirmed by science, helping us repair the metabolism that is gradually losing speed, delaying the anxiety of cells, and allowing those states that we “thought could only endure” to be gradually replaced by mildness.
We just want to quietly explain more clearly the three ways the human body absorbs NMN: oral, intravenous and nebulized.
Tell you their different principles, effects and application methods, so that you can know how to make scientific choices when you are truly conscious and need to take care of yourself.
David Sinclair, a professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School, once said, “We grow old not because of the passage of time, but because cells lose their ability to repair themselves.”
What exactly is NMN that has taken world by storm
Let’s get straight to the point. Friends over 35 years old, do you often hear the term NMN? As expected, this term is often associated with anti-aging.
Many people have asked Daohe Platform what the mechanism of action of NMN is and whether it really has an effect on anti-aging.
What exactly is NMN
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a derivative of vitamin B3 and a direct “precursor” of the coenzyme NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) in the human body.
Precursors refer to substances that can be transformed into target molecules through a series of reactions in the human body.
As a precursor of NAD+, NMN indicates that it is an upstream substance in the process of NAD+ synthesis. Once inside the body, it can be rapidly converted into NAD+, thereby participating in functions such as energy metabolism and cell repair.
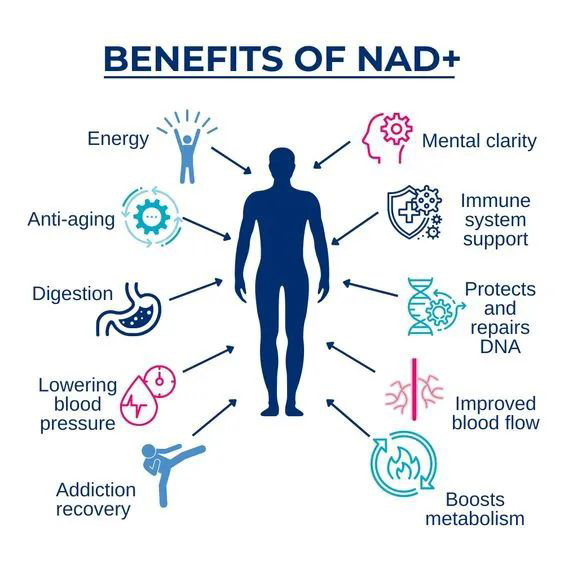
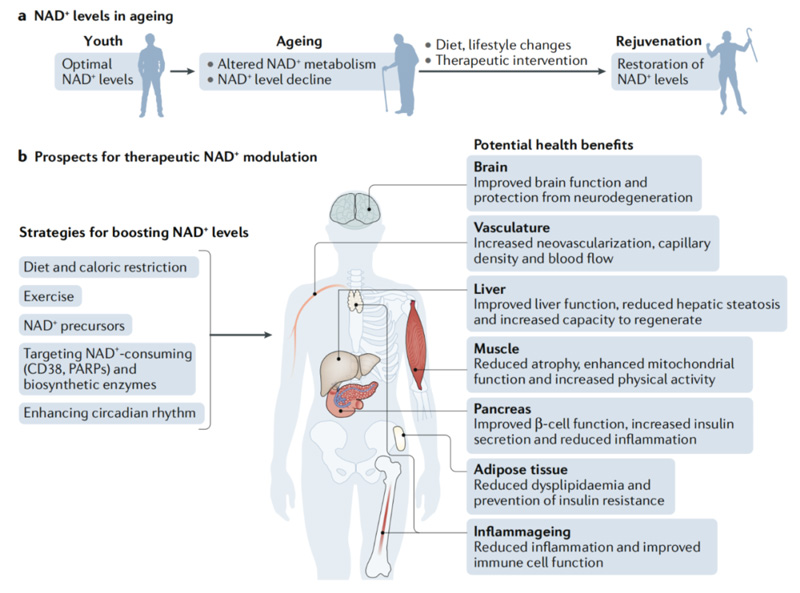
NAD+ is a coenzyme involved in various key physiological processes such as cellular energy metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation, but its level significantly decreases with age.
The research of David Sinclair, a professor at Harvard University, has drawn global attention to NMN.
His team discovered that by supplementing NMN to increase the level of NAD+, longevity proteins (such as Sirtuins) could be activated and certain aging indicators reversed.
How did NMN quickly become popular
In a well-known mouse experiment that changed people’s perception of NMN, after older people mice were supplemented with NMN for two months, their capillary density returned to a youthful level, their muscle endurance increased by 56-80%, and their running endurance rose from an average of 240 meters to 430 meters.
Even older mice that used NMN in combination with hydrogen sulfide precursors ran twice as long as the untreated group.
These achievements have led NMN to be hailed by the media as the “hope substance for reversing aging”, triggering global acclaim.
More importantly, a large number of cell and mouse experiments have demonstrated the potential of NMN in anti-aging and health improvement.
For instance, long-term (12 months) oral administration of NMN can inhibit age-related weight gain, enhance energy metabolism, increase insulin sensitivity, and improve age-related gene expression changes, bringing the metabolism and energy levels of mice close to those of a younger state.
In the field of neurology, research has found that increasing intracellular NAD+ levels has extensive benefits for the survival and function of neurons.
A team from the Baltimore Institute on Aging in the United States and the University of Oslo in Norway administered NMN to models of premature aging and Alzheimer’s disease.
The results showed that NMN promoted DNA repair and selectively cleared damaged mitochondria, protected neurons from abnormal protein toxicity, and improved memory and extended healthy lifespan in mice.
These studies (published in “Cell Metabolism”, “Nature Neuroscience”, etc.) provide strong support for the anti-aging mechanism of NMN.

A test data of older people in Japan
Some studies have indicated that supplementing NMN may improve fatigue and sleep quality in the older people:
A clinical trial involving 108 older people in Japan showed that after supplementing 250mg of NMN every afternoon for 12 weeks, the muscle strength of the lower limbs improved and the feeling of daytime sleepiness was significantly reduced.
The improvement effect of mental fatigue in the older people who took the medicine in the afternoon was particularly prominent.
Although human evidence for specific areas such as memory and sleep is still limited, the improvement in cell function brought about by NMN enhancing NAD+ is considered highly likely to contribute to overall health.

Overall, due to the fact that NMN can replenish the NAD+ that decreases with age, improve cellular energy and anti-damage ability, and backed by research from authoritative institutions such as Harvard, NMN has rapidly gained global popularity.
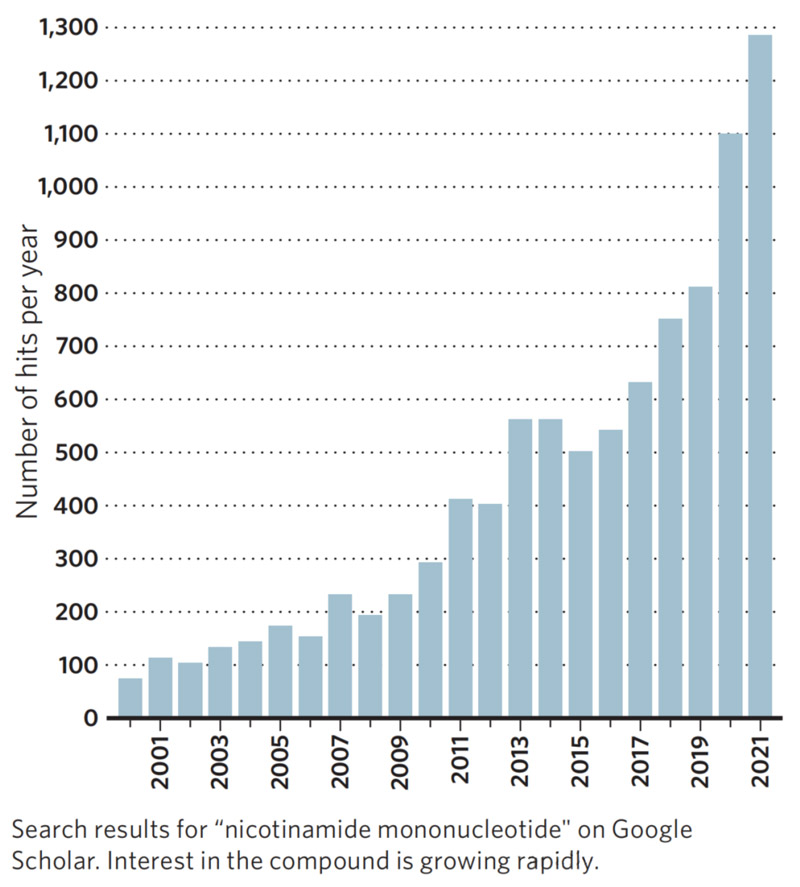
Since 2015, NMN has frequently mentioned in academic literature and popular science.
The market for related nutritional supplements has grown rapidly from 253 million US dollars in 2020 and expected to reach 386 million US dollars by 2027.
The prospects of NMN indeed very promising, but the real data on its anti-aging effects in the human body still accumulated. The frequency of discussions about NMN worldwide is increasing day by day every year.
technical advantages and institutional background of NMN in Japan
After NMN became popular worldwide, enterprises in various countries launched related products one after another.
In terms of product quality and clinical norms, the NMN industry in Japan demonstrates unique advantages.
The leading purity of raw materials and the preparation process.
Japanese manufacturers were the first to achieve large-scale and high-purity production of NMN. Many Japanese brands claim that the purity of NMN exceeds 99%, approaching the medical-grade standard.
In July 2020, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan officially included NMN in the list of “food ingredients (non-pharmaceutical)”, making its legal application in health food products.
Japan thus became the first country in the world to approve NMN as a food ingredient.
Before this, NMN regarded as a drug in Japan and subject to approval. As a food ingredient, it regulated by food regulations, requiring producers to ensure quality and safety.
This policy shift has promoted the compliance and high quality of NMN products in Japan.

Japan has a free diagnosis and treatment policy that supports the clinical application of NMN and a complete intervention medical system.
Free medical treatment also a frequently asked question on the Daohe platform and in our comment section.
The so-called “free medical treatment” refers to the fact that under the Japanese medical system, doctors can offer certain treatments with insufficient clinical data in self-funded (not covered by medical insurance) items.
In the field of NMN, many clinics have launched NMN intravenous injection as a free medical treatment project.
The free medical treatment program can used by physicians under their responsibility.
That is to say, Japanese regulations allow practicing doctors to provide anti-aging therapies such as NMN intravenous drip to clients in need, as long as they inform and sign the informed consent.
This policy provides a legal platform for the experimentation and application of cutting-edge anti-aging technologies.
Medical care in Japan divided into three categories: insured medical care, free medical care, and advanced medical care.
The state covers 70% of the cost of insured medical treatment, while individuals only need to bear 30%. However, for the self-paid portion of free medical treatment and advanced medical care, patients have to pay the full amount (10%) themselves.
NMN intravenous drip, nebulization and other treatments fall within the category of “free diagnosis and treatment”, and thus not covered by medical insurance. Patients must bear the full cost themselves.
The intervention (prevention) medical system in Japan is relatively mature, and both the public and doctors have a high acceptance of anti-aging medical treatment.
Due to their rich experience in clinical trials and practical applications, Japanese doctors have a better understanding of the dosage, effects and risks of NMN, and have also developed a preliminary intervention plan.
For instance, some clinics and doctors recommend intravenous infusion of NMN as a periodic treatment course (once every 1 to 4 weeks) to maintain health and delay aging.
The compliance and reliability of the NMN market in Japan are relatively higher.
On the one hand, the Japanese government strictly regulates the advertisements and efficacy claims of health products. Enterprises dare not exaggerate the effects at will, and consumers also pay more attention to scientific evidence.
On the other hand, most NMN products in Japan produced in accordance with the GMP standards of pharmaceutical companies, and the purity and test reports clearly marked on the packaging.
In Japan, NMN supplements regulated by the Food Hygiene Act and other laws due to their status as food ingredients, and enterprises required to file for record.
Under this institutional background, the quality of NMN products in the Japanese market more guaranteed, and clinical applications mostly carried out under the supervision of doctors.
This has made Japan regarded by the industry as a leader in the application of NMN, leading Europe and the United States in terms of credibility and safety.
On the one hand, Japan encourages innovative applications; on the other hand, it adopts a cautious attitude towards scientific evidence.
The technological and institutional advantages of NMN in Japan offer the public a high-quality and relatively reliable option, but it still advocates rational and science-based use.
A Detailed Explanation of Three Usage Methods of NMN
At present, NMN mainly used in three ways in the field of anti-aging: oral administration, intravenous drip and nebulized inhalation.
They each have their own characteristics in terms of absorption pathways, bioavailability efficiency, onset time and applicable populations.
1. Take NMN orally
① Absorption pathway: Oral administration is currently the most common and convenient way to supplement NMN.
After being taken orally as capsules or powder and entering the gastrointestinal tract, NMN is mainly absorbed in the small intestine, then enters the liver through the portal vein for metabolism, and is released into the bloodstream.
Scientists have discovered that there is a specialized transport protein in the small intestine that can directly transport NMN molecules into intestinal cells, thereby efficiently absorbing NMN.
However, oral absorption also has individual differences and certain limiting factors.
Some studies have pointed out that different tissues take in oral NMN to varying degrees, and the intestinal flora may break down some NMN, thereby reducing the actual amount entering the circulation.
The bioavailability of oral NMN is not 100%, but it can still significantly increase the level of NAD+ in the body at a reasonable dose.
② Conversion efficiency and onset time: It usually takes a certain amount of time for oral NMN to take effect after digestion and absorption.
When taken on an empty stomach, the level of NAD+ precursors in the blood will start to rise approximately 30 minutes to 1 hour and distributed to various tissues within a few hours.
Compared with the immediate effect of intravenous drip, the release of the effect of oral NMN is relatively mild and gradual.
However, continuous daily use can create homeostasis in the body and increase the basal NAD+ level.
A phase I clinical trial conducted by Keio University in Japan administered a single oral dose of 100-500mg of NMN to 10 healthy volunteers. The results showed that NMN effectively metabolized in the body without any obvious adverse reactions.
Although the trial did not report a significant increase in plasma NAD+ concentration, a series of NAD+ metabolites detected to increase, indicating that oral NMN has utilized by the body.
In a subsequent randomized controlled trial on postmenopausal women, taking 250mg of NMN orally daily for 10 weeks found that the sensitivity of skeletal muscle to insulin improved, suggesting that oral NMN may have a certain effect on improving energy metabolism in the human body.
Overall, oral NMN has a moderate efficiency in enhancing NAD+ and bringing about functional improvements.

③ Safety and physical burden: As the most natural way of intake, oral administration currently considered to have a relatively high level of safety.
NMN is present in foods such as broccoli and edamame, but in extremely low amounts. Therefore, taking it orally as a nutritional supplement is essentially similar to taking vitamins.
In the existing human trials (100-500mg once and 250mg daily for 10 consecutive weeks), no serious adverse reactions have reported for oral NMN.
However, it should noted that since NMN can increase the metabolic level of NAD+, people with gout or hyperuricemia (related to purine metabolism), as well as pregnant and lactating women, minors and other special groups should use it with caution or avoid it, as there is still a lack of research data for these groups.
Overall, it is quite safe for normal adults to take NMN orally and has a minimal physical burden. This is one of the reasons why it is popular as a health supplement.

④ Applicable population and convenience: Oral NMN is almost suitable for all people who wish to enhance their health and vitality and delay aging, especially young and middle-aged people and those in the early stage of anti-aging.
For those who are busy with daily work and cannot frequently visit Japanese clinics, taking a few NMN capsules every morning is undoubtedly the most convenient solution.
The oral method is private and simple, does not require professional equipment or venues, and is easy to take for a long time consistently. This makes it the preferred way for the majority of consumers.
Oral NMN is suitable for daily health care and long-term intervention. For young people who focus on prevention or those trying NMN for the first time, taking it orally is a good start.
However, it should noted that reliable brands and appropriate dosages should selected under the guidance of a doctor or nutritionist.
Taking advantage of the popularity of NMN, many mixed brands have emerged in the market. Many of these products have extremely low active ingredients, which may lead to no effect at all after long-term use, thus affecting the reputation of NMN in society.

2. Intravenous infusion of NMN
① Absorption route: Intravenous drip is a method of directly inputting NMN into the bloodstream in solution form, thus there is no loss in digestion and absorption, and the theoretical bioavailability is nearly 100%.
When NMN slowly injected into the vein, it immediately spreads throughout the body via the bloodstream. Unlike oral administration, it bypasses the liver’s first-pass metabolism and can expose the entire body’s tissues to high concentrations of NMN and the subsequently converted NAD+ in a short period of time.
That is to say, intravenous injection of NMN can deliver NMN throughout the body within minutes and gradually convert and enhance NAD+ in tissues.
Studies have found that the injected NMN can cross the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain tissue (such as the thalamus), thereby exerting its effect in the central nervous system.
This point holds potential significance for improving brain aging, as only a limited portion of NMN/NAD+ through the oral route enters the brain, while intravenous drip can rapidly increase NAD+ in the brain.
This is also a major advantage of intravenous administration: it is widely and rapidly distributed, and there is no absorption bottleneck.

② Transformation efficiency and onset time: The onset of NMN by intravenous drip is almost immediate.
In clinical practice, NMN usually prepared into a solution of a certain concentration and infused into the body through intravenous drip for 15 to 60 minutes.
The commonly used dosage in some anti-aging clinics is about 300mg each time.
According to a clinical report from Japan, after healthy individuals received an intravenous infusion of 300mg of NMN, the level of NAD+ in their blood increased significantly by approximately 20%, and this increase was accompanied by biological effects in the body – for instance, the level of triglycerides (TG) in the blood decreased significantly after the injection.
Researchers believe that since the intravenous drip route avoids the decomposition of NMN in the digestive tract, its effect is far superior to that of oral administration and can exert a more effective metabolic improvement effect.
Intravenous injection of NMN can also activate the NAD+ synthesis pathway in the body: It has observed that the level of the key enzyme NAMPT increases after NMN injection, suggesting that the body may have initiated the nicotinamide recycling pathway to continuously synthesize NAD+.
This means that a single drip not only instantaneously increases NAD+ but may also drive the body to increase NAD+ production for a longer period of time.
In conclusion, intravenous infusion of NMN can reach the peak of blood drug consumption in a short period of time and trigger a series of beneficial metabolic changes, with extremely high conversion and utilization efficiency.
③ Safety and physical burden: Intravenous administration is an invasive procedure and carries certain risks and discomfort compared to oral administration.
In the trial in Japan, 10 healthy adults received a single intravenous injection of NMN (at a safe dose), and no abnormal changes observed in subsequent monitoring of electrocardiogram, blood pressure, liver and kidney functions, etc.
Hematological examinations also found no damage to red blood cells or white blood cells. The vital signs of the subjects were stable and no serious adverse reactions occurred, indicating that intravenous infusion of NMN is generally relatively safe.
It is also encouraging that the study observed a significant decrease in triglycerides after NMN injection without any adverse changes. From this, its speculated that NMN is very likely to have a preventive effect on lipid metabolism disorders.
It should noted that a single intravenous infusion is equivalent to instantly administering a large amount of NMN to the body.
For those who are very old or have multiple underlying diseases, it should carried out with caution after a doctor’s assessment to avoid excessive metabolic fluctuations in a short period of time.
④ Target population and convenience: Intravenous NMN infusion usually targeted at people who have a higher demand for anti-aging or hope for quick results.
For instance, middle-aged and older people, especially those of advanced age, due to their weakened absorption function and low cellular NAD+ levels, can more effectively increase NAD+ through intravenous drip.
Therefore, many middle-aged and older people and those with financial means choose to regularly receive NMN intravenous drips at qualified clinics in Japan as a way to “maintain” their health.
Those who have already developed aging-related health issues (such as metabolic syndrome and cognitive decline) and wish to improve in the short term may also benefit from the therapy, as it can provide high doses of NMN directly to the target tissue within a few hours.
Intravenous injection relatively expensive and inconvenient: it needs to carried out at a qualified medical institution after being evaluated by a doctor. Each process takes about half an hour to one hour and requires a short period of observation.
This approach mostly chosen by those who have better economic conditions and are willing to invest in health.
It is not suitable as a daily routine but more like a monthly or quarterly reinforcement supplement.
Intravenous infusion of NMN usually adjusted under the guidance of a doctor in combination with physical examination indicators, making it more suitable for use within the medical framework rather than being done at will by individuals.
3. Nebulized inhalation of NMN
① Absorption pathway: Nebulized inhalation involves dissolving NMN in a sterile solution and using a nebulizer to spray it into a micron-sized aerosol, which then absorbed into the body through the oral and nasal mucosa.
It’s somewhat similar to the spray inhalers used by asthma patients.
Its absorption route lies between oral administration and intravenous drip.
After atomization, NMN particles directly enter the pulmonary capillary network through the respiratory tract epithelium, and some can also reach the brain through the olfactory nerve pathway of the nasal mucosa.
NMN nebulization therapy can deliver NMN through the nose to the hypothalamus area of the brain.
The hypothalamus is the center for hormone regulation and metabolic control in the human body and is closely related to the aging process.
If NMN can directly enter the hypothalamic cells, is expected to rapidly affect the body’s metabolism and aging mechanisms.
In contrast, oral NMN requires a long process of digestion and systemic circulation for a small portion to act on the brain, while the nasal absorption pathway shortens this process.
Nebulized inhalation enters the bloodstream as quickly as intravenous injection and acts on the respiratory center and the brain like nasal spray, which can regarded as a dual path.
Based on the experience of other drugs, the inhalation route feasible for water-soluble small molecules, so the NMN aerosol should effectively absorbed.
② Transformation efficiency and onset time: The onset speed of nebulized inhalation of NMN expected to second only to intravenous drip, the active ingredients usually enter the bloodstream and tissues within a few minutes.
Because the lungs provide a huge exchange interface, once the drug solution reaches the alveoli, it will pass through the thin alveolar membrane and enter the circulation almost instantaneously.
The same is true for the absorption of the nasal mucosa. Many drugs (even vaccines) can take effect within 5 to 10 minutes when administered by nasal spray.
After NMN inhaled through nebulization, the NAD+ level in the blood expected to rise in a short period of time, especially the increase in NAD+ in the brain may more rapid and direct.
From the perspective of pharmacokinetics, the utilization efficiency of inhaled NMN should higher than that of oral administration (without gastrointestinal degradation loss), but it may slightly lower than intravenous injection (because the absorption through the lungs into the blood still requires a diffusion process, and the absorption amount affected by breathing depth, atomization particle size, etc.).
③ Safety and physical burden: Nebulized inhalation of NMN is a non-invasive administration and relatively safe, but attention should paid to the tolerance of the respiratory system.
The aqueous solution of NMN itself is nearly neutral and will not irritate the mucous membranes. Most people should have no obvious discomfort when inhaling it.
For those who have never had nebulization before, the first use may cause slight irritation to the throat, coughing or runny nose, etc. Generally, these symptoms will subside after adaptation. Based on the current application feedback, no serious side effects of NMN inhalation have reported.
The main group of people who need attention are those with lung diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Inhaling any substance rashly may induce bronchospasm. Therefore, such people should use it with caution or under the supervision of a doctor.
There is a lack of data on atomized NMN in pregnant women and patients with serious diseases. Its not recommended to try it on your own.
Overall, nebulized inhalation imposes a minimal direct burden on the body, without the pain of acupuncture or the burden on the stomach and intestines. It is a mild and safe method of drug administration.

④ Applicable population and convenience: NMN nebulized inhalation is more suitable for people who are reluctant to receive injections but hope for quick results.
A typical example is some middle-aged office workers who feel tired but are afraid of intravenous injection. They can choose to do an NMN nebulization “deep breathing” during their break. Its said that it can quickly refresh the mind and relieve fatigue.
Some users who pay attention to brain health care may interested in inhaling NMN because it may act more directly on the brain, improving concentration and memory.
In terms of convenience, if an individual has a portable nebulizer, its not complicated to inhale it at home following the instructions. Some clinics in Japan also provide it.
Each treatment lasts approximately 10 to 15 minutes and is quiet and non-invasive.
For instance, there are medical clinics in Japan that offer multiple inhalations of NMN for one course of treatment, with charges comparable to intravenous drips.
Overall, nebulized inhalation is suitable for those who wish to get an injection more quickly but do not want it, especially for middle-aged and older people with mild cognitive or sleep problems who hope to improve their brain function.

A summary of the comparison of three methods
Based on the above analysis, we can briefly compare the characteristics of the three NMN usage routes: oral, intravenous, and nebulized as follows:
1. Absorption efficiency
Intravenous > Nebulization > oral administration. Direct vein entry into the blood is the most complete. Most of the atomization enters the blood, with only a small amount of loss. Oral administration is affected by digestion and has the lowest actual utilization rate.
2. Onset speed
Intravenous ≈ nebulization (minute level) > oral administration (hour level). Both intravenous drip and inhalation can rapidly increase NAD+, and the oral effect is gradual.
3. effect lasts
Oral administration can maintain a stable level as its taken continuously every day. The single effect of intravenous and nebulization is relatively short and requires intermittent administration for maintenance.
4. Safety risk
Oral administration has the lowest risk (similar to food), nebulization requires attention to respiratory hygiene, and intravenous administration is an invasive operation, but it is within a controllable range.
5. Degree of convenience
It is most convenient to take orally and can used daily. Atomization requires equipment support; It takes more time to go to a medical institution for intravenous treatment.
6. Applicable object
Oral administration is suitable for a wide range of people as long-term health care. Veins are suitable for those with strong anti-aging needs and significant improvement requirements.
Nebulization is suitable for those who do not want intravenous drips but need to enhance the effect and can be used as an auxiliary.
Summary and Suggestions
NMN, as a highly sought-after anti-aging nutrient in recent years, has indeed demonstrated exciting effects in experimental research.
The three usage methods of oral administration, intravenous drip and nebulized inhalation each have their own advantages and offer choices for people with different needs.
So which way suits you best?
1. General middle-aged and young people and those who are encountering it for first time
It is recommended to take oral NMN.
It is safe, convenient, cost-effective and suitable for long-term persistence. Start with a low dose, such as 100-300mg per day, and gradually adjust according to your feeling.
Combined with a healthy diet and exercise, it can serve as the basic plan for anti-aging and health care.
When taking oral medication for a long time, it is necessary to choose products from regular manufacturers and pay attention to their purity and qualifications.
2. Middle-aged and older people who pursue more significant effects
Intravenous infusion of NMN can be attempted under the assessment of a professional doctor.
Especially for those over 60 years old with obvious signs of aging (such as metabolic syndrome and memory decline), it is advisable to consider undergoing an intravenous drip treatment once a month or once a quarter to rapidly increase the NAD+ level in the body.
However, it is necessary to ensure that it is carried out in a qualified medical institution by an experienced doctor, and that indicators such as liver and kidney functions are checked before the operation.
Intravenous drip therapy is a medical intervention. Its effect should be evaluated in combination with regular physical examinations and should not be used frequently or excessively (it is generally recommended to use it at intervals of several weeks or more).
3. Those who are not convenient for intravenous injection but wish to improve their mental state immediately
Nebulized inhalation of NMN can serve as a beneficial supplement.
For instance, middle-aged people who often need mental work and feel exhausted can have an NMN nebulization before important activities to enhance their concentration and alertness.
Of course, this requires contacting platforms like Daohe in advance and the compliant institutions providing this service.
There is currently a lack of data on nebulization therapy, and its effects vary from person to person. It is recommended to use it as an added bonus and cannot replace the anti-aging strategy of the system.
No matter which way is chosen, long-term persistence and combination with good living habits are the key.
No matter how magical NMN is, it cannot make up for the damage caused by a long-term unhealthy lifestyle.
Whether taken orally, by drip or by nebulization, the effect of NMN is based on long-term persistence and scientific management.
It is neither an immediate miracle drug nor a universal shield against time. Instead, it is an auxiliary tool that enhances the efficiency of cell repair and delays physiological decline.