NAD+ is a necessary molecule in the process of phage infection, and the elimination of NAD+ will hinder the replication of phage.
Bacteria use a variety of anti-phage defense systems to defend against phage infection, and a series of recent studies have demonstrated that many of these defense systems can consume NAD+ in response to infection by breaking down intracellular Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) into ADP-ribose (ADPR) and nicotinamide.
On September 25, 2024, researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel published a research paper entitled “Phages reconstitute NAD+ to counter bacterial immunity” in the top international academic journal Nature.

The study uncovered a unique new immune escape strategy for viruses (phages) by resynthesizing NAD+ to fight the bacteria’s antiviral defense system, and they were able to rebuild NAD+ depleted by the bacteria’s antiviral defense system, thereby overcoming host (bacterial) immunity.
The study revealed that a significant number of phages possess enzymatic pathways capable of resynthesizing NAD+ from their degradation products in infected cells.
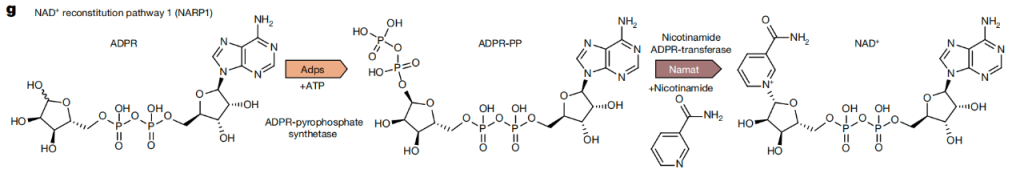
The second enzyme (Nicotinamide ADPR-transferase) combines ADPR-PP with nicotinamide to form NAD+.
The study describes the NAD+ Reconstitution Pathway 1 (NARP1), a two-step process in which an enzyme (ADPR-PP synthetase) phosphorylates ADP-ribose (ADPR) to produce ADPR pyrophosphate (ADPR-PP).
Narp1-encoding phages are able to overcome a range of bacterial antiviral defenses (including Thoeris, DSR1, DSR2, SIR2-HerA, and SEFIR defenses), all by depleting NAD+ as part of their defense mechanisms.
Phylogenetic analysis revealed that NARP1 is predominantly present in the phage genome, suggesting that it has phage-specific functions in countering bacterial defense mechanisms.
The second pathway, NARP2, allows the phage to synthesize NAD+ by using a different metabolite than ADPR-PP, thus overcoming the bacteria’s antiviral defense mechanism.
This study shows that viruses (phages) employ a unique immune escape strategy in which they are able to rebuild NAD+ depleted by the bacteria’s antiviral defense system, thereby overcoming host (bacterial) immunity.
About GSHWORLD
Anhui GSH Bio-technology Co., Ltd. was incorporated in Anqing High-tech Industrial Development Zone in 2017. The company is an innovative high-tech enterprise with enzyme catalysis technology in the field of synthetic biology as the core and multi-disciplinary technology cross-application.
The company has gathered a technical team of overseas returnees, university professors, industry experts and other fields such as enzyme engineering, fermentation engineering, molecular biology, AI technology, chemistry, materials science, pharmacy and engineering.
The company’s technical application of enzymatic production of pharmaceutical raw materials has subverted the traditional fermentation method, truly achieved environmental protection and energy saving, green production, and occupied a leading position in the market of characteristic raw materials.
The company is a global pioneer of enzyme-catalyzed coupled ATP regeneration technology, with a number of independent intellectual property rights, has been granted 6 national invention patents, another under review of more than 10 invention patents, 2 PCT patents.