Synthetic biological raw materials | The new generation of natural antioxidant hydroxytyrosol has a market size of 1.5 billion, CAGR 24.4%, and the highest reported output is 9.8g/L
Introduction to Hydroxytyrosol
Hydroxytyrosol widely found in olive plants and considered a functional ingredient in various food matrices and widely added to edible oils, beverages, meat products and dairy products.
DCR-HT has many important medicinal properties, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory, chondroprotective, and anti-osteoporotic properties.
Hydroxytyrosol mainly extracted from the leaves and fruits of the olive plant, however, extraction from this method involves long extraction cycles, low recovery rates and seasonal changes in raw material sources.
Therefore, microbial cell factories that synthesize DCR-HT have attracted widespread attention in recent years.
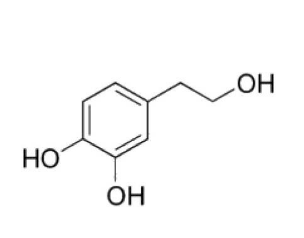
The chemical name of Hydroxytyrosol (HT) is 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol, and its molecular formula is C8H10O3.
The molecular structure of hydroxytyrosol not only has a phenolic hydroxyl group like other phenolic substances, but also has an alcohol use disorder hydroxyl group on the ethanol chain connected to the benzene ring. It is an iridoid hydroxyaromatic compound.
Hydroxytyrosol considered to one of the most efficient active antioxidants, with strong antioxidant activity and pharmaceutical effects.
Hydroxytyrosol is also a free radical scavenger that can effectively remove endogenous and exogenous free radicals and oxidants. Compared with other natural antioxidant compounds (green tea, Q10 coenzyme, quercetin), hydroxytyrosol Stronger ability to scavenge free radicals and antioxidants.
In addition, hydroxytyrosol not only reduces the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids and fatty acids, but also reduces the metabolism of linoleic acid, vitamin A, sphingolipids and arachidonic acid, while increasing the metabolism of glycerides.
Compound information
Manufacturer
The main companies include Beijing Tiankaiyida Bio-Technology Co.,LTD., Anhui GSH Bio-Technology Co.,LTD., Jilin Aoteng Bio-Technology Co.,LTD., Jilin GSH Bio-Technology Co.,LTD., Shenzhen GSH Bio-Technology Co.,LTD., etc., among which, Shaanxi Senyuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou Weibo Lai Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and Shaanxi Fuheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. have larger production capacity and output. They are the leading companies in the domestic hydroxytyrosol industry and have a high market share.
Market size
In addition to the direct use of hydroxytyrosol as a nutritional and functional substance, some of its derivatives, such as oleuropein, acetylated derivatives of hydroxytyrosol, derivatives with polyunsaturated fatty chains, etc. Applied research is also ongoing.
Against the backdrop of growing market demand for hydroxytyrosol, global hydroxytyrosol production technology has become increasingly mature, and the global market has steadily expanded.
According to data released by New Thinking, the global hydroxytyrosol market will exceed 1.5 billion yuan in 2021.
In 2020, China’s demand for hydroxytyrosol is 42.92 tons, with a growth rate of 24.4%.
global drivers
From the perspective of the global market, the research and production of hydroxytyrosol in Europe and the United States started early. The U.S. Food Safety Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Administration (EFSA) have issued regulations on olive polyphenols (hydroxytyrosol is the most important olive polyphenol). The positive view of the health benefits of hydroxytyrosol products has greatly promoted the market vitality of hydroxytyrosol products. Products containing hydroxytyrosol have been launched abroad one after another.
For example, the product Polyphen-oiTM of the American Life Extension company, the OleaselectTM product of the Italian Indena company, the HytoliveTM product of the Spanish Genosa company, the ProlivolsTM product of the French Seppic company, and the HIDROXTM jointly developed by the American CreAgri company and the Dutch DSM company.
Hydroxytyrosol regulations
China’s hydroxytyrosol industry has a small development scale and has not received enough attention. Industry-related standards are lacking. The relevant national standards are mainly “Olive Oil, Olive Pomace Oil” (GB/T 23347-2009), and relevant enterprise standards include Zhejiang Shaoxing Family According to the “Olive Leaf Extract Enterprise Standard” (Q/SJZ0005S-2019) of the Biological Products Co., Ltd., industry development restricted by relevant policies and standards. Analysts at New Thinking believe that the lack of standards has led to a low degree of standardization in the domestic hydroxytyrosol industry. There are no unified specifications for products in terms of technical indicators and quality indicators, and product quality is uneven, hindering the healthy development of the industry.
Biosynthetic maximum yield
The article “Promoting FADH2 Regeneration of Hydroxylation for High-Level Production of Hydroxytyrosol from Glycerol in Escherichia coli” shows that there are several biosynthetic pathways for hydroxytyrosol, mainly the intermediate steps from p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate to hydroxytyrosol.
The central metabolite p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate synthesized from simple carbon sources through the glycolysis pathway and the shikimate pathway, and then undergoes sequential reactions such as dehydrogenation, hydroxylation, transamination or deamination to produce hydroxytyrosol.
This study constructed the de novo biosynthesis pathway of hydroxytyrosol in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) and analyzed the effect of blocking the competitive pathway on the biosynthesis of hydroxytyrosol. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae dehydrogenase ADH6 introduced to increase the flux of p-hydroxytyrosol.
In order to strengthen the key hydroxylation effect, L-amino acid deaminase (LAAD) derived from Proteus mirabilis introduced to promote the conversion of FAD to FADH2 and achieve further accumulation of hydroxytyrosol. Considering the various cofactors involved in hydroxytyrosol biosynthesis, a cofactor cycle was constructed to increase the supply of the cofactor FADH2. Finally, by optimizing the carbon source, pH and seed culture medium, using glycerol as the carbon source for batch culture and fermentation in a 5L fermenter, the final yield of hydroxytyrosol was 9.87 g/L.
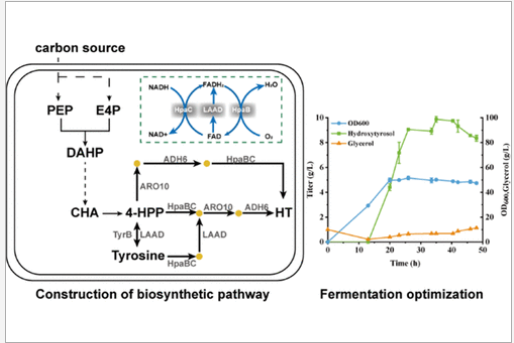
This is the highest yield reported so far and provides new ideas for microbial production of hydroxytyrosol.