The rapid growth of the market has also led to the melee between various types of “NAD+ supplements”, NMN, NR, NA, NAM, NADH, dazzling, these “NAD+ supplements” in the end which is strong?
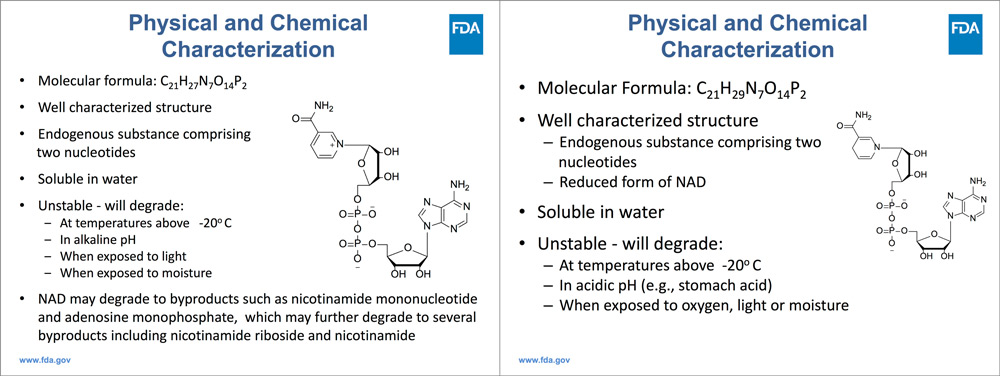
NAD/NADH: unstable
NAD+ is the oxidizing form and its reducing form is NADH.
However, both NAD+ and NADH are very unstable, according to the US FDA description, NAD+ / NADH will decompose when the temperature is higher than “minus 20 degrees Celsius”, and is afraid of light, afraid of wet, afraid of oxidation, NADH is afraid of acidic environment (such as stomach acid), and NAD+ is afraid of alkaline environment.
Such unstable properties, coupled with excessive molecular weight, make direct supplementation of NAD+ ineffective.
Scientific research has focused on supplementing the precursors of NAD+ and converting them into NAD+ in the body.
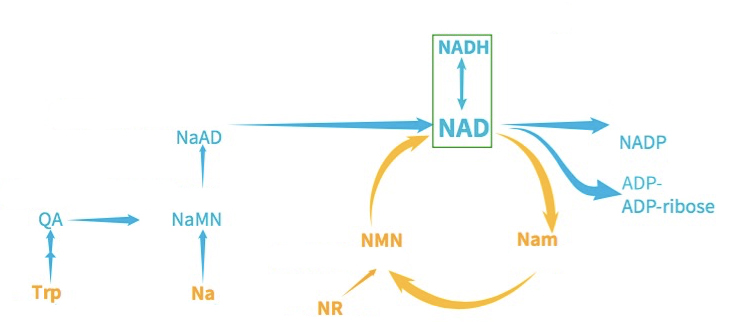
The precursors of NAD+ include NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide), NA (niacin), NAM (nicotinamide), NR (nicotinamide ribose), Trp (tryptophan), etc.
Tryptophan (Trp) : The synthetic pathway is blocked
Tryptophan is one of the essential amino acids (provided by food) in the body, it is a precursor of serotonin and is found in dairy products, meat, brown rice, fish and soy.
There are three main metabolic pathways of NAD+ in vivo: de novo synthesis pathway, Preiss-Handler pathway, and remediation pathway.
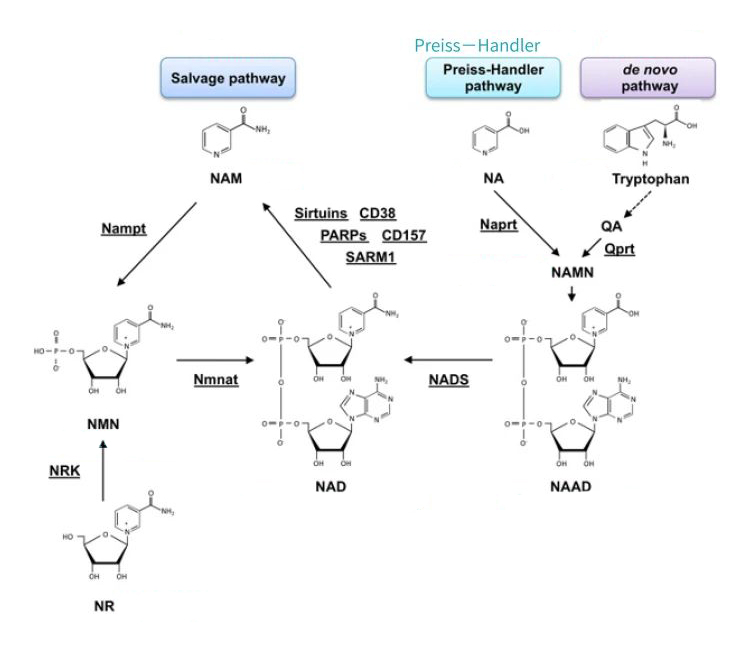
The pathway of tryptophan synthesis of NAD+ is “de novo synthesis pathway”, which uses tryptophan ingestion from food to enter the Preiss-Handler pathway after several steps, and then syntheses NAD+ after a series of complex reactions.
Because of the complexity of the synthesis pathway, the NAD+ generated by de novo synthesis and Preiss-Handler pathway only accounts for a small part of the total NAD+ in human body, and the synthesis of NAD+ mainly comes from the remedial synthesis pathway (NMN, NR, NAM belong to this pathway).
Niacin (NA) : Not necessarily effective and not necessarily safe
Niacin (NA), vitamin B3, is one of the 13 essential vitamins for the human body, which is a water-soluble vitamin, and NA can be converted into NAM (niacinamide) in animals.
Natural NA can derived from animal organs or muscle tissue, but also from fruits, vegetables, seeds, fungi and so on.
Many foods are rich in NA, so the average person is not deficient in NA.
In June 2020, a clinical study using NA as a precursor of NAD+ to treat mitochondrial myopathy reported in the sub-journal Cell, which was the first clinical study report using NA as a precursor of NAD+.
Patients given daily doses of NA ranging from 250 mg to a maximum of 1000 mg for up to 10 months and showed an increase in NAD+ in their blood.
However, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Big Data statistics:
Large doses of NA (more than 30 mg) may cause side effects, and excessive doses (1,000 mg) are more likely to cause adverse reactions such as low blood pressure, nausea, abdominal pain, vision impairment, eye fluid accumulation, and hyperglycemia.
The synthesis of NAD+ by NA in vivo is through the Preiss-Handler pathway. Supplementing NA does not necessarily enter the target cell directly to become the raw material of NAD+, but needs to go through other complicated steps.
Therefore, supplementing NAD+ with NA is not an effective and safe method.
Nicotinamide ribose (NR) : limited effect, health effects are questionable
Nicotinamide ribose (NR) occurs naturally in milk and dairy products and was first discovered by scientists in 1944.
In 2004, NR used in anti-aging research as a precursor of NAD+, and industrialization began in 2012.
NR in its natural form is extremely unstable, and all NR currently used in dietary supplements is in its chloride form.
NR needs to converted to NMN before NAD+ synthesized in vivo, so the synthesis efficiency is not high.
Most of the current research papers on NR clinical trials have shown that NR can increase NAD+ levels in blood, but not in muscle.
The physiological effect of NR on NAD+ limited, and direct supplementation may improve NAD+, but it may not appear in the right place at the right time, and the overall health effect is doubtful.
Niacinamide (NAM) : The conversion efficiency is low and the effect decays with time
Niacinamide (NAM) is an amide compound of niacin (NA), which is abundant in lean meat, beans, fish and peanuts.
Although NAM can enhance NAD+ in some cells, the synthesis efficiency is not high, and the effect decreases with age, pressure and other factors. The conversion of NAM to NAD+ is limited by the rate-limiting enzyme NAMPT, and the activity of long-life protein Sirtuins is inhibited.
It found that NAM remained in rats for a shorter time than NMN.
NAM can cause nausea and flushing, and has reported to cause liver toxicity when taken in high doses.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) : the direct precursor of NAD+, with high absorption conversion
Research surrounding NMN has published in more than 100 scientific journals, and animal studies have shown that it has a variety of anti-aging effects and is safe and non-toxic.
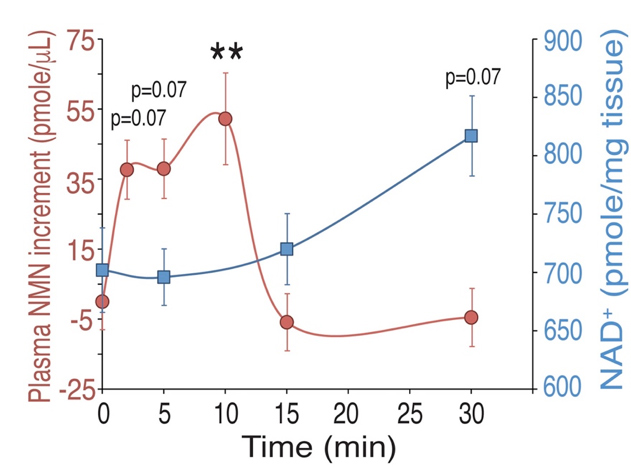
In 2016, research conducted by Professor Shinichiro Imai’s team at the University of Washington found that:
- After oral administration of NMN, it enters the bloodstream within 2-3 minutes
- Increase NMN levels in the body within 15 minutes
- Increase NAD+ within 30 minutes
In February 2020, human safety trials published in the Endocrine Journal showed that a single dose of 500 mg of NMN is safe, and no adverse effects have reported in other ongoing clinical trials.
It can seen from the transformation path of various NAD+ precursors that NMN a direct precursor of NAD+, which easily absorbed by cells and can efficiently supplement NAD+, and its distribution and bioavailability in organisms are better than other precursors, which is currently an ideal supplement for NAD+.