Can staying up late be saved? Studies have found that melatonin can improve DNA damage repair after staying up late and reduce cancer risk
Sleep is one of the body’s repair processes.
About one third of a person’s life is spent in sleep, good sleep is one of the three health standards recognized by the international community, and sleep time is too short or poor sleep will affect health.
In today’s society, staying up late has become the norm for many young people.
Often staying up late will bring great harm to the body, and lack of sleep is closely related to accelerated aging, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and increased risk of cancer.
Melatonin, a hormone secreted by the pineal gland in the brain, plays an important role in regulating the body clock and sleep cycle.
Exogenous melatonin supplementation known to help regulate sleep timing, and can also used to improve sleep difficulties in night shift workers due to circadian rhythm disturbances, or to alleviate jet lag.
However, it was not clear whether melatonin supplementation improved DNA damage repair in night shift workers.
On February 24, 2025, Researchers from Columbia University published a paper in the journal Occupational and Environmental Medicine entitled “Melatonin supplementation and oxidative DNA damage repair capacity among night shifts. workers: a randomised placebo-controlled trial “research paper.
Studies have shown that melatonin supplementation improves the ability of night shift workers to repair DNA damage, suggesting that melatonin supplementation may be a viable intervention strategy to reduce the cancer risk faced by night shift workers.

In this parallel randomized placebo-controlled trial involving 40 night shift workers, participants randomly assigned to either melatonin supplementation or placebo, melatonin supplementation (3 mg) given before daytime sleep (after night shift) for 4 weeks, and urine samples collected to assess 8-OH-dG concentrations.
We analyzed whether melatonin can improve DNA damage repair in night shift workers.
8-OH-dG, an indicator of DNA damage repair ability, a chemical produced when cells repair DNA damage, and the higher the concentration, the better the repair ability.
The results found that the melatonin group had 1.8 times higher concentrations of 8-OH-dG in their urine during daytime sleep compared to the control group, indicating a greater ability to repair DNA damage during daytime sleep.
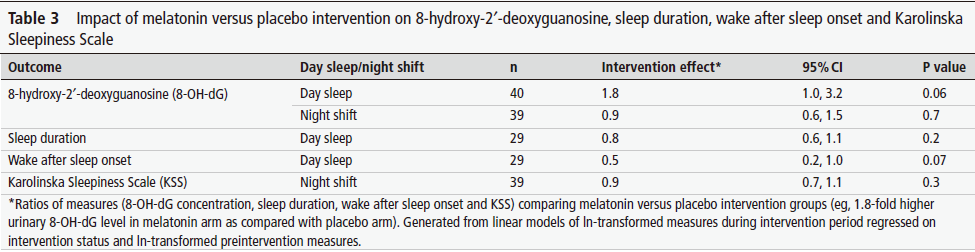
Analysis of melatonin levels found that during daytime sleep, circulating melatonin levels in the melatonin supplement group were significantly higher than those in the placebo group, averaging 90.8 ng/mg versus 1.5 ng/mg in the placebo group.
On subsequent night shifts, circulating melatonin levels in the melatonin supplement group decreased significantly, but remained higher than those in the placebo group.
Previous studies have shown that melatonin may promote the recognition and repair of 8-OH-dG damage by up-regulating the expression of genes associated with the nucleotide excisable repair (NER) pathway.
This randomized controlled trial suggests that melatonin supplementation may improve DNA damage repair in night shift workers and may reduce the risk of cancer faced by night shift workers.
It is worth mentioning that melatonin supplementation also contributed to the risk of cardiovascular disease in female nurses who worked long shifts.
Before that, Researchers from Harvard University published an article in the journal Lancet diabetes & Endocrinology entitled “Use of melatonin supplements and risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in the USA: insights from three prospective cohort studies “.
The study showed that among female nurses who worked long-term shifts (more than 5 years), melatonin supplementation associated with a 38% lower risk of cardiovascular disease.

References:
- https://dx.doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2024-109824
- https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587 (24), 00096-2