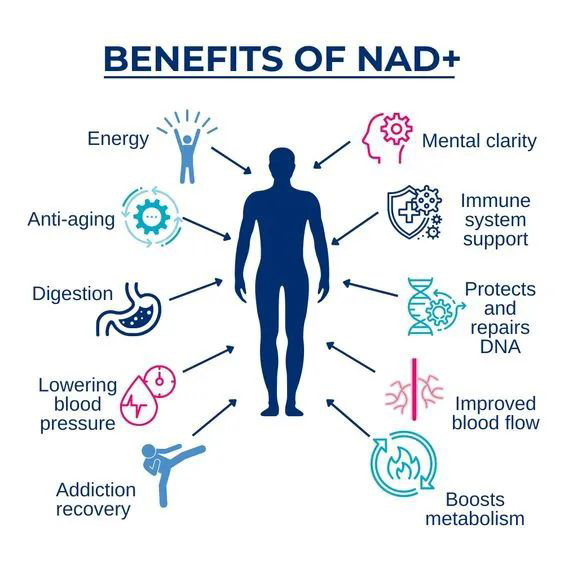
NMN is a direct precursor of NAD+ and can be rapidly converted to NAD+ through specific enzymatic reactions, thus playing a variety of important roles in the human body, including activation of human cells.
1. Energy metabolism
NMN can enhance the energy metabolism capacity of cells, mainly by increasing the level of intracellular NAD+.
NAD+ is a key coenzyme in mitochondrial metabolism, participating in energy metabolism processes such as oxidative phosphorylation and helping cells convert nutrients (such as glucose, fatty acids, etc.) into energy (ATP).
Adequate energy supply is essential for the normal physiological functions of cells, including material synthesis, cell division, cell migration, and intracellular material transport.
Supplementing with NMN can increase ATP production and improve the energy supply of cells, thereby activating cells and maintaining their normal function.
2. Promotes DNA repair

In the normal physiological process, cells are constantly affected by endogenous and exogenous factors, resulting in the occurrence of DNA damage.
Common types of DNA damage include base damage, single strand break and double strand break.
In order to maintain the stability of the genome, cells have a variety of DNA repair mechanisms, such as base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, mismatch repair and double-strand break repair.
By increasing the level of intracellular NAD+, NMN can enhance the activity of repair enzymes such as PARP (polyADP-ribose polymerase) and SIRT1 (deacetylase), thereby promoting the DNA repair process, reducing the impact of DNA damage on cells, and maintaining the health and vitality of cells.
3. Anti-oxidative stress
Cells produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) during metabolism, such as superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals.
When ROS is generated too much or the cell’s antioxidant defense system is damaged, oxidative stress will occur, causing lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation and DNA damage, and then affecting the normal function and survival of cells.
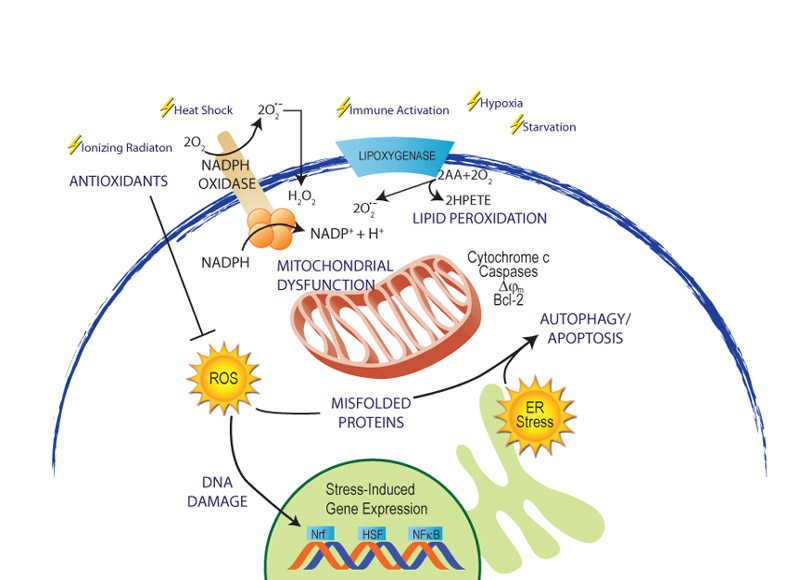
Supplementation of NMN can activate the activity of SIRT1 and other antioxidant enzymes, improve the antioxidant capacity of cells, reduce the accumulation of ROS and oxidative stress damage.
This antioxidant effect helps protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress, thereby activating and maintaining normal cell function.
4. Regulating mitochondrial function
Mitochondria are the “energy factories” within the cell, responsible for producing ATP to maintain the normal physiological function of the cell.
By increasing the level of NAD+, NMN can activate a series of NAD+ dependent enzymes, especially Sirt3 and other deacetylases, to help restore the function of mitochondrial proteins and improve the work efficiency of mitochondria.
NMN can also promote the activation of mitochondrial biosynthesis pathway, promote mitochondrial regeneration and repair, thereby increasing the number and improving the quality of mitochondria.
These effects help maintain the young state and functional integrity of mitochondria, providing adequate energy supply and metabolic balance for cells.
5. Regulate telomere function
Telomeres are structures at the ends of chromosomes that protect the stability and integrity of chromosomes.
As the number of cell divisions increases, the telomeres will gradually become shorter, and when it is short enough, the cell will stop dividing and enter a state of aging.
By increasing NAD+ levels, NMN can enhance energy metabolism and gene expression within cells, thereby helping to maintain telomere stability and function.
NMN can also activate the sirtuins protein family, which can directly act on telomere related proteins to regulate their expression levels, thereby promoting telomere repair and preventing DNA damage.