Studies have found that NMN can safely increase the level of NAD+ in middle-aged men, improve metabolism, alleviate hyperinsulinemia, may be beneficial to cardiovascular health, and has a tendency to improve sleep, but more studies are needed to confirm its long-term effect and dose-response relationship.
Recently discovered, the international Journal Endocrine Journal published a study article on the safety and effects of NMN in healthy middle-aged men.
The research team systematically summarized the role of NMN as a nutritional supplement in metabolism, sleep, and NAD+ biosynthesis, and explored its potential application in cardiovascular health, highlighting the close association between NMN supplementation and cardiovascular protection.

The study was an 8-week, single-center, single-arm, open-label clinical trial involving 11 healthy middle-aged Japanese men who received 125 mg NMN capsules twice daily before breakfast.
The study evaluated the safety, biochemical, metabolic, ophthalmic, and sleep quality parameters of NMN supplementation, as well as temporal changes in NAD+ levels in peripheral tissues.
The results are as follows:
NMN Improves NAD+ metabolism
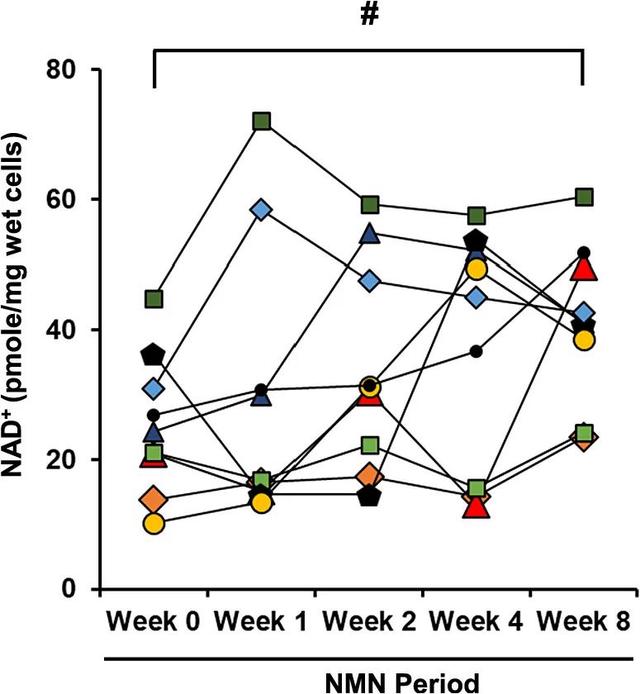
The study data showed that after NMN supplementation, the levels of NAD+ in participants’ peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) increased significantly.
This suggests that oral NMN can be effectively absorbed and progressively enhance NAD+ metabolism in peripheral tissues over time.
Oral NMN is an effective way to increase the level of NAD+ in the body.
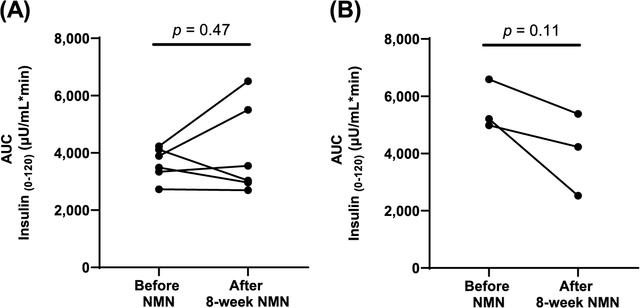
Relieve postprandial hyperinsulinemia
The results of the study showed that the volunteers in the study showed good tolerance to NMN supplements.
And in participants, especially those with excessive insulin secretion after oral glucose load (n = 3), NMN modestly reduced postpranpranal hyperinsulinemia, an important risk factor for coronary artery disease.
This finding suggests that NMN may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health by improving insulin secretion and action.
NMN Affect sleep quality
The researchers initially assessed sleep quality using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI).
Although NMN supplementation did not result in a statistically significant change in PSQI score, there was a trend to suggest that subjective sleep quality improved with increasing duration of NMN supplementation.
Another study showed that in human beings aged 45 to 75 years with sleep disorders, oral administration of 300mg of NMN daily for 10 weeks improved sleep quality as assessed by PSQI.
In human clinical trials over the age of 65, participants who consumed 250mg/ day of NMN after 6 PM for 12 weeks were also observed to improve sleep quality.
Because sleep quality in this study assessed using a subjective questionnaire, it cannot completely said that NMN does not have the potential to improve sleep quality.
To further assess the effect of NMN on sleep, an EEG analysis required and each sleep stage analyzed.
Security assessment
The study also evaluated the safety of NMN.
The results showed that in healthy middle-aged Japanese men, supplementation with 250 mg of NMN daily for 8 weeks generally safe and tolerable, and no significant side effects observed. This suggests that at this dose, NMN is a relatively safe health supplement.
Sum up
This study laid a solid foundation for the clinical application of NMN.
But future research needed to further explore the long-term effects of NMN on different populations, as well as its potential role in preventing and treating age-related diseases.
Further studies on the dose-response relationship, time of administration and individual differences of NMN also needed to optimize the clinical use of NMN.